命令形式
API格式
在 kibana 中执行
1 | GET /_cat/health?v |
curl访问API
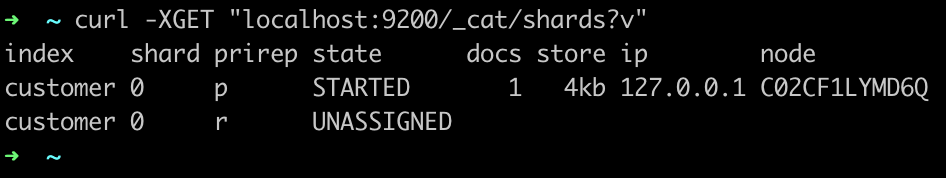
在 terminal 中执行
1 | curl -XGET "localhost:9200/_cat/shards?v" |
集群操作
获取健康信息
1 | ## output |
获取分片信息
1 | curl -XGET "localhost:9200/_cat/shards?v" |
获取节点信息
1 | curl -XGET "localhost:9200/_cat/nodes?v" |
索引操作
命令末尾追加pretty,可以漂亮地打印JSON响应(如果有的话)
创建索引
1 | curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/customer?pretty' |
查询索引
显示所有索引信息, 若索引太多,建议重定向到文件中,避免终端显示不完整
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v' > tmp.log
1 | curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v' |
删除索引
1 | curl -XDELETE 'localhost:9200/customer?pretty' |
文档操作
Elasticsearch并不要求,先要有索引,才能将文档编入索引。创建文档时,如果指定索引不存在,将自动创建
创建文档
将一个客户文档放到 customer 索引中, ID 为1
1 | ##API: |
查询文档
在 customer 索引中查询 文档 id 为 1 的数据
1 | curl -XGET "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty" |
更新文档
Elasticsearch实际上并没有在底层执行就地更新,而是先删除旧文档,再添加新文档
修改数据
将 customer 索引中文档 ID 为 1 的 name 更改为 “Jane Doe”
1 | curl -XPOST "localhost:9200/customer/_update/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
添加字段
把文档(ID为1)中的name字段更改为 “Altman”,再添加一个年龄字段: age
1 | curl -XPOST "localhost:9200/customer/_update/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
脚本执行
使用脚本将年龄增加5岁
1 | curl -XPOST "localhost:9200/customer/_update/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
删除文档
删除文档 ID 为 2 的数据,注 该 ID 不存在
1 | curl -XDELETE "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/2?pretty" |
批处理
先将 customer 索引删除,重建,然后执行下面
某个操作失败不会导致批量API执行中断,剩下的操作将继续执行。当_bulk API返回时,它将为每个操作提供一个状态(与发送操作的顺序相同),以便检查某个特定操作是否失败。
在一个批量操作中,创建两个文档
1 | curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/_bulk?pretty' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' |
在一个批量操作中,更新第一个文档,删除第二个文档
对于delete操作,只需提供被删除文档的ID即可
1 | curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/_bulk?pretty' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' |


